The Shift From Conversation to Execution
Enterprises have moved beyond experimenting with generative AI solutions and chatbots. The conversation phase is over. The execution phase has begun.
AI coworkers, also called AI assistant agents or autonomous AI agents, are now capable of acting inside enterprise systems. They can read documents, update CRM records, generate code, reconcile invoices, schedule workflows, trigger API calls, and even delete files.
This is not incremental productivity improvement. This is workflow compression.
CIOs and CTOs are now asking:
- How do we deploy AI assistant agents securely?
- What governance model is required?
- What are the real enterprise risks?
- How do we prevent over-permissioned AI systems?
- Can we audit autonomous AI decisions?
This blog provides direct answers. No hype. No fluff. Just execution-level clarity.
What Are AI Coworkers?
AI coworkers are autonomous or semi-autonomous AI assistant agents that can execute tasks across enterprise systems, not just generate text.
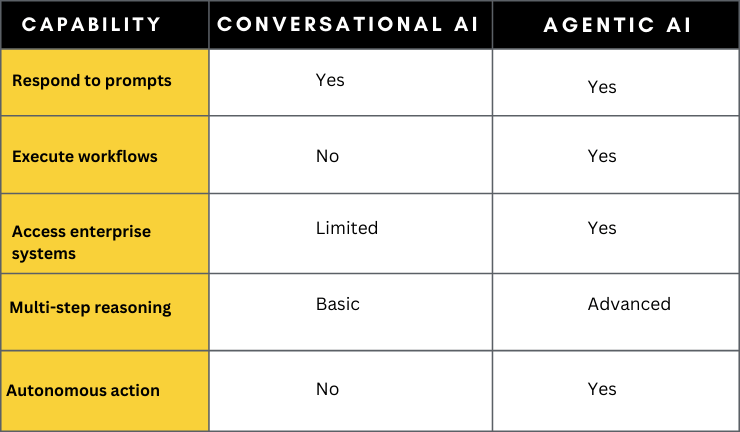
Unlike traditional chatbots that respond to prompts, agentic AI systems:
- Maintain memory across workflows
- Use tools and APIs
- Make conditional decisions
- Execute multi-step tasks
- Interact with databases and SaaS platforms
This marks the transition from conversational AI to agentic AI.
Conversation vs Agentic Execution
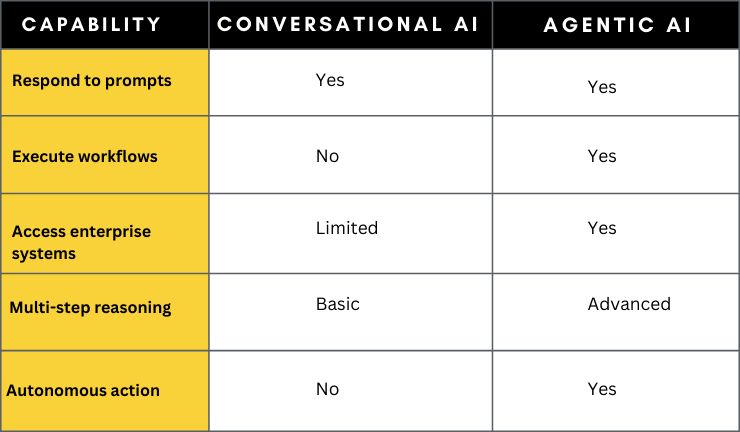
For enterprise leaders, the question is not whether AI coworkers are coming. They are already here. The question is whether you will govern them properly.
The Productivity Gains: Enterprise Workflow Compression
Workflow Compression Across Complex Enterprise Processes
Enterprise workflows are traditionally fragmented across systems, approvals, and manual checkpoints. A single process often requires data retrieval, validation, documentation, email coordination, and system updates. AI coworkers compress these multi-day workflows into minutes by orchestrating tasks across ERP, CRM, HRMS, DevOps, and finance platforms. Instead of handing off tasks between departments, autonomous AI agents execute them sequentially and in parallel, eliminating latency between steps. The result is measurable cycle-time reduction and faster operational throughput.
Automated Cross-System Orchestration
Modern enterprises operate in a multi-system environment where data lives in silos. AI assistant agents bridge these silos. They can pull data from an ERP system, validate it against compliance rules, update financial records, trigger approval workflows, and generate reporting dashboards in one coordinated sequence. This orchestration reduces manual system switching, minimizes human error, and ensures consistent policy enforcement across platforms. The impact is not incremental efficiency. It is structural productivity improvement.
Reduced Operational Overhead and Error Rates
Manual processes introduce delays and inconsistencies. Human-driven data entry, reconciliation, and documentation create operational drag and risk exposure. AI coworkers execute rule-based decisions with high consistency and speed. They do not fatigue, overlook fields, or skip validation steps. This reduces error rates in invoice processing, compliance reporting, IT ticket resolution, and customer onboarding. Enterprises gain higher accuracy while simultaneously lowering operational overhead.
Acceleration of Decision Cycles
Decision-making in large organizations often stalls due to fragmented information. AI assistant agents aggregate and synthesize structured and unstructured data in real time. Instead of waiting for reports to be compiled, leaders receive contextual insights instantly. This acceleration shortens planning cycles, improves responsiveness to market changes, and strengthens competitive positioning. Faster execution becomes a strategic advantage, not just an operational benefit.
Human and AI Collaboration at Scale
AI coworkers do not eliminate the need for human in loop expertise in software development. They elevate it. By automating repetitive and rules-driven tasks, AI agents free skilled professionals to focus on strategic analysis, innovation, and exception management. Humans review high-risk decisions, refine strategy, and manage stakeholder relationships, while AI executes operational workflows. This structured delegation model enables enterprises to scale output without proportionally increasing headcount.
Enterprise-Wide Productivity Multiplier
When AI assistant agents are deployed across finance, HR, IT, DevOps, customer operations, and compliance, the cumulative impact compounds. Each compressed workflow contributes to organization-wide efficiency gains. Instead of isolated automation wins, enterprises achieve systemic acceleration. This is where agentic AI shifts from experimentation to enterprise transformation.
The Real Risks of AI Assistant Agents
The same capabilities that drive productivity also introduce new classes of risk. Enterprise leaders must treat AI coworkers like privileged digital employees.
1. Over-Permissive Access and Autonomous File Deletion Risk
One of the most underestimated risks in agentic AI is excessive system permissions.
If an AI coworker has:
- Read and write access to shared drives
- Admin-level SaaS permissions
- Database modification rights
It can:
- Delete critical files
- Modify financial records
- Trigger destructive API calls
Autonomous execution without guardrails can lead to operational disruption.
Key risk: AI agents do exactly what they are instructed to do. They do not question business logic unless explicitly programmed to validate it.
2. Prompt Injection Attacks
Prompt injection is a security vulnerability where malicious input manipulates the AI agent’s behavior.
Example scenarios:
- A document contains hidden instructions telling the AI to exfiltrate data
- A user request overrides internal system rules
- External content influences enterprise workflows
Unlike traditional software vulnerabilities, prompt injection targets the reasoning layer.
Enterprises must implement:
- Input sanitization
- Role-based instruction boundaries
- Tool access validation
- External content isolation
Without these controls, AI coworkers can be socially engineered.
3. Auditability Challenges
When a human makes a decision, you can ask why. When an autonomous AI agent executes 27 API calls across 5 systems in 12 seconds, can you explain:
- Why it made each decision?
- What data influenced it?
- What alternative paths were rejected?
Auditability is now a board-level concern.
Key governance requirements include:
- Decision logging
- Traceable reasoning steps
- Version-controlled prompts
- Immutable audit records
If you cannot explain it, regulators will question it.
4. Compliance and Regulatory Risk
Industries such as healthcare, fintech, and government face:
- Data privacy laws
- Sector-specific compliance mandates
- Cross-border data restrictions
Autonomous AI execution must comply with:
- Data minimization policies
- Access segmentation
- Jurisdictional controls
An AI coworker operating across global systems without geographic constraints can unintentionally violate regulatory frameworks.
Enterprise AI Strategy: How to Adopt Agentic AI Safely
Phase 1: Use Case Prioritization
Start by identifying AI workflows that are high volume, rules-driven, and operationally repetitive. The strongest candidates for agentic AI are cross-system processes that consume time but require limited subjective judgment. Avoid high-risk financial or regulatory actions in the initial phase and focus on controlled efficiency wins.
Phase 2: Controlled Pilot
Deploy AI assistant agents within a sandboxed or limited production environment to test execution reliability. Measure accuracy, exception rates, workflow latency, and system behavior under real conditions. The objective is validation, not scale, ensuring the agent performs predictably before expanding access.
Phase 3: Governance Hardening
Before enterprise rollout, strengthen governance controls around access, audit logging, escalation workflows, and security testing. Implement role-based permissions, injection safeguards, and approval gates for sensitive actions. This phase ensures that automation does not outpace compliance and risk management.
Phase 4: Enterprise Scale
Once validated and secured, expand deployment across departments under centralized oversight. Standardize monitoring dashboards, maintain model version control, and continuously assess performance drift. Scaling agentic AI responsibly requires ongoing governance, not a one-time deployment event.
How ISHIR Helps Enterprises Deploy AI Coworkers Securely
ISHIR helps enterprises design and deploy secure AI coworkers and autonomous AI agents with a governance-first architecture built for scale. As an AI-powered digital product engineering company, we implement enterprise AI automation, role-based access control, and advanced AI governance frameworks to ensure compliance, auditability, and operational safety. Our approach integrates secure API orchestration, prompt injection protection, and continuous monitoring to mitigate real-world AI security risks. From strategy to production rollout, ISHIR enables organizations to accelerate AI workflow automation without compromising data protection, regulatory requirements, or enterprise-grade controls.
Enterprise workflows are slowing execution, AI coworkers can unlock speed & scale
ISHIR builds secure, auditable, enterprise-grade AI assistant agents that deliver real productivity without unmanaged risk.
Frequently Asked Questions About AI Coworkers
Q. What is an AI coworker?
An AI coworker is an autonomous or semi-autonomous AI assistant agent that can execute enterprise tasks across systems, not just generate responses.
Q. How is agentic AI different from generative AI?
Generative AI produces content. Agentic AI can execute multi-step workflows, use tools, and take actions inside enterprise environments.
Q. Are AI assistant agents secure?
They can be secure if built with proper governance, role-based access control, prompt protections, and audit logging. Without these, they introduce risk.
Q. What is prompt injection?
Prompt injection is a security attack where malicious input manipulates an AI agent’s instructions, potentially causing unauthorized actions.
Q. Can AI coworkers delete files or modify systems?
Yes, if they are granted those permissions. That is why least-privilege access and approval gates are critical.
Q. How do you audit AI decisions?
Through structured logging, traceable reasoning steps, and immutable execution records tied to each action the AI performs.
Q. What industries benefit most from AI assistant agents?
Healthcare, fintech, SaaS, logistics, and enterprise IT operations see high ROI due to complex workflows.
Q. How long does it take to deploy enterprise AI agents?
A controlled pilot can be deployed in weeks. Enterprise-wide rollout depends on governance and integration complexity.
Q. Do AI coworkers replace employees?
No. They augment teams by automating repetitive workflows and enabling humans to focus on strategic work.
Q. What is the biggest risk of agentic AI?
Over-permissioned autonomous systems executing destructive or non-compliant actions without adequate oversight.
Q. How do enterprises control autonomous AI systems?
By implementing strict IAM policies, human-in-the-loop validation, and comprehensive monitoring.
Q. What is workflow compression in AI automation?
Workflow compression is the reduction of multi-step, multi-day processes into minutes using AI-driven orchestration.
Q. Is AI governance mandatory for enterprise deployment?
Yes. Without governance, auditability, and compliance controls, AI deployment introduces unacceptable risk.
Q. Can AI coworkers operate across global teams?
Yes, especially when designed with distributed engineering support and region-aware data policies.